2022. 8. 9. 20:00ㆍ개발공부 기강잡자/Git
과거로 돌아가기 - reset과 checkout
1. reset

이 상황에서 commit "4"에서 "3" (2f86ae9796c71873d055f01d324979fce1e4cecf)으로 돌아가고 싶을 경우, 다음과 같은 명령어를 사용한다.
git reset --hard 2f86ae9796c71873d055f01d324979fce1e4cecf> 가장 최신 commit은 2f86ae9796c71873d055f01d324979fce1e4cecf으로 바뀌게 된다.
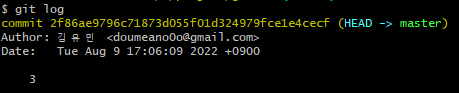
= refs/heads/master에 기록되어있는 object id 가 변함 (가장 최신 commit id 변경)
∴ reset을 한다 = checkout 하고 있는 branch의 최신 커밋을 바꾸는 것
Q : 그렇다면 4번 commit은 지워진걸까?
A : 아니다! > reset 취소해서 다시 4번으로 돌아가기 가능!
logs/refs/heads/master에는 master branch에서 일어나는 history를 기록하고 있음
reset 시에도 "4" commit에서 "3" commit으로 reset 되었다는 것도 기록 되어있다.- 또한, 정보를 잃을 수 있는 위험한 명령을 하기 전에, git은 ORIG_HEAD파일에 현재 head가 가리키고 있는 object id 를 기록한 후에 명령을 수행하기 때문에 reset 취소 가능
git reset --hard ORIG_HEADreset 명령을 취소하고 싶을 때, ORIG_HEAD의 값으로 reset 명령을 하면

다시 "4" commit으로 돌아온 것을 확인할 수 있다.
git reflog
: 각각의 commit 의 log가 기록되어있다. 이 정보를 통해 이전 명령으로 돌아갈 수 있다.
commit log을 확인한 후, git reset에 되돌아가길 원하는 commit의 commit hash 값을 주어 되돌릴 수 있다.

git reset --hard 2f86ae9> 2f86ae9 해시 값을 가진 commit으로 reset
2. checkout
git checkout {commit_id}: commit의 object id으로 checkout 가능

HEAD가 commit을 직접 가리킬 수 있다. => detached 된 상태 ('detached HEAD' state)
reset 시, working directory, index, repository 영역
git reset [-- hard | -- soft | -- mixed] 옵션별 reset 범위
| Working directory = Working tree = Working copy : 실제 작업을 진행하는 곳 |
index = staging area = cache : git add 했을 때, 추가 되는 곳 |
Repository = history = tree : commit 버전이 저장되는 곳 |
git reset --soft: repository의 history만 취소 |
||
git reset --mixed: index와 repository만 취소 |
||
git reset --hard: 모두 초기화 |
f1.txt의 데이터가 각 영역별로 아래와 같을 때, 명령어의 각 옵션을 수행한 결과를 살펴보자.
| Working directory | index | Repository | |
초기값vim f1.txtgit addgit commit |
"init" | "init" | "init" |
vim f1.txtgit commit -am |
"repository" | "repository" | "repository" |
vim f1.txtgit add |
"index" | "index" | "repository" |
vim f1.txt(최종 상태) |
"working copy" | "index" | "repository" |
1. git reset --soft {commit_id}
git reset --soft {commit_id}: repository만 취소되고, index와 working directory의 상태는 그대로 유지된다.
✔ git log -p 명령을 통해 repository 에서의 f1.txt 내용을 확인해보자.
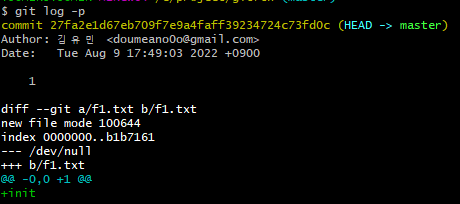
> repository의 f1.txt 내용이 "repository"에서 "init"으로 되돌아간 것을 확인할 수 있다.
✔ git diff 명령을 통해 f1.txt의 index와 working directory의 상태를 확인해보자.

> f1.txt의 index의 내용과 working directory의 내용은 그대로라는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
* git reset --soft {commit_id} 명령을 취소하여 "repository"로 복원할 경우에는,
git reset ORIG_HEAD 명령어는 default 옵션이 mixed 이기 때문에 index와 repository 의 f1.txt 내용이 모두 "repository"로 복원되기 때문에 주의해야한다.
git reset --soft ORIG_HEAD 해야 git reset --soft {commit_id} 명령 취소를 올바르게 할 수 있다.
∴ --soft는 repository만 reset 한다
2. git reset --mixed {commit_id} (default)
git reset --mixed {commit_id}: repository와 index의 상태가 취소되고. working directory의 상태는 그대로 유지된다.
✔ reset 명령어 수행 후, git log -p 명령을 통해 repository 에서의 f1.txt 내용을 확인해보자.

> repository의 f1.txt 내용이 "repository"에서 "init"으로 되돌아간 것을 확인할 수 있다.
✔ git diff 명령을 통해 f1.txt의 index와 working directory의 상태를 확인해보자.
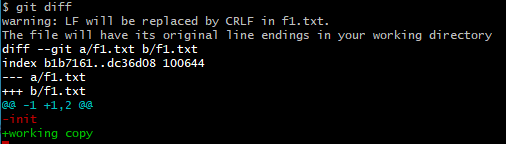
> index의 f1.txt 또한 "index"에서 "init"으로 취소된 것을 확인할 수 있고, working directory의 내용은 "working copy" 그대로라는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
∴ --mixed는 index와 repository를 reset 한다
3. git reset --hard {commit_id}
git reset --hard {commit_id}: repository, index, working directory의 상태가 모두 취소 .
✔ reset 명령어 수행 후, git log -p 명령을 통해 repository 에서의 f1.txt 내용을 확인해보자.

> repository의 f1.txt 내용이 "repository"에서 "init"으로 되돌아간 것을 확인할 수 있으며,

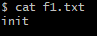
> index와 working directory의 내용이 모두 "init"으로 되돌아간 것을 확인할 수 있다.
∴ --hard는 working directory, index, repository를 모두 reset 한다
본 게시물에 문제가 있을 경우, 댓글로 알려주세요.
참고 : 지옥에서 온 git - 이고잉 님 강의
'개발공부 기강잡자 > Git' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Git - 지옥에서 온 git] 5일차 - 원격 저장소 remote repository (0) | 2022.08.11 |
|---|---|
| [Git - 지옥에서 온 git] 4일차 - git의 원리 공부 (merge/conflit/3-way merge) (0) | 2022.08.09 |
| [Git - 지옥에서 온 git] 4일차 - git의 원리 공부 (branch와 HEAD) (0) | 2022.08.09 |
| [Git - 지옥에서 온 git] 3일차 - branch 수련 (git-scm의 Documentation 보기) (0) | 2022.08.04 |
| [Git-지옥에서 온 git] 3일차 - branch (0) | 2022.08.04 |